If you are suffering from loss of hearing or perhaps one or both of your ears are itching or aching despite having tried out everything you possibly could to improve and resolve the symptoms, then you have a buildup of earwax that should be treated by a professional.
Good news is, here at Gees Chemist, we are now offering Microsuction Ear Wax Removal Service by our expert and professionally trained pharmacists.
Why Microsuction?
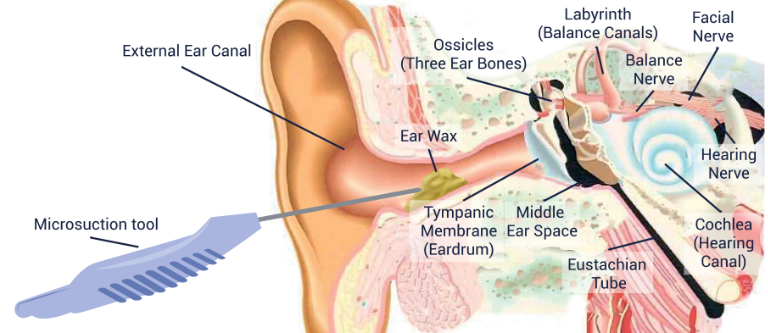
Microsuction is the most modern, advanced, safest, and pain-free form of ear wax removal. It is the most effective and safest form of earwax removal as it avoids touching the sensitive area around the ear canal and avoids contact with the eardrum.
This method does not use high pressure water suction as seen with a syringing technique, therefore allowing it to be the safest, fastest and cleanest method of Ear Wax Removal.
What is the Procedure?
We strongly advise our patients to apply one to two drops of olive oil into their affected ear/s, for at least 5 days prior to but not on the day of the treatment.
We will take a comprehensive medical history of the patient on the day of the appointment to ensure patient's safety.
After a microscopic examination of the inner ear canals and ear drums, the Pharmacist will use a low pressure suction probe in order to gently and safely remove earwax. The Pharmacist will wear a pair of illuminated microscopes, namely ‘loupes’, and air will be heard rushing through the suction wand during the procedure. There may be an occasional mild ‘pop’ as the wax is sucked through the probe. Generally, the appointment will be painless resulting the patient with better hearing and healthy ears!
Treatment Prices
- Consultation fee (no wax): £20
- Microsuction For One Ear: £40
- Microsuction For Both Ears: £60
Walk in Service for consultation is available at the Pharmacy. You can Also Book an appointment in advance by giving us a call or send us an email to book an appointment.
Please note that, Payment will be collected at the pharmacy on the day of the appointment.
If you are overweight and are serious about losing weight, the Lipotrim Pharmacy Programme could help you reach your goal, knowing you have a highly trained healthcare professional on hand for information, advice and encouragement.
- You need to be overweight and serious about losing it .
- There are a few medical restrictions so you will need to fill out a medical screening form at the pharmacy to make sure the programme is suitable for you.
- If you are accepted for the programme, you will have to attend the pharmacy weekly for weight measurements and, where possible at the pharmacy, a urine test to measure ketones.
- The pharmacy is also where you will pick up weekly supplies of Lipotrim products.
- An essential short video/DVD and written materials are available to assist you on the programme.
- This programme is pharmacy-based and run by the pharmacist. It is not available for over the counter sale or mail order.
FACIAL HAIR REMOVAL
Advice, support and treatment for women living with facial hair
DID YOU KNOW?
Female facial hair is extremely common. In fact, around 5-15% of women are currently living with some degree of excess hair.
For many women, obvious or excess facial hair can be a source of both distress and embarrassment. While all women have some degree of facial hair, it is usually light and unnoticeable. For some women however, the hair can be darker or thicker than usual. This can make it more obvious — something many women find upsetting.
Living with unwanted facial hair can cause a significant knock to your self-esteem and confidence, stopping you from socialising and enjoying recreational outings and activities.
Thankfully, for women who are bothered by their facial hair, there are ways to treat it. Read below for more details on the causes of unwanted facial hair, and the proven treatments available.
CAUSES OF UNWANTED FACIAL HAIR
Up to 15% of women are currently living with excess hair[1]. Although unwanted facial hair itself is not dangerous to your health, it can be a sign of an underlying condition. There are several potential causes of unwanted facial hair in women, and understanding these conditions can give you a clearer idea of what kind of treatment is necessary in order to effectively get rid of your unwanted facial hair.
The most common of these possible causes include polycystic ovary syndrome, hirsutism and facial hair as a result of hormone imbalance. Each of these conditions carry a different set of symptoms, but all involve some degree of excess facial hair.
PCOS
PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) is a common condition which impacts the way a woman’s ovaries work. It is defined by three main symptoms, which are:
- Polycystic ovaries: the ovaries themselves become enlarged and house many fluid-filled sacs known as follicles. These surround the eggs.
- Irregular periods: meaning your ovaries aren’t regularly releasing eggs.
- Excess androgens: these are high levels of ‘male hormones’ in the body, leading to physical symptoms like excess facial and body hair.
It is not known exactly what causes PCOS but it does tend to run in families. There is also no cure for the condition, though a healthy lifestyle can help combat symptoms, and you can treat symptoms like facial hair individually.
HIRSUTISM
Hirsutism is one of the most common causes of unwanted facial hair in women, as it causes excessive hair growth in certain areas of the body, including the:
- Face
- Neck
- Stomach
- Chest
- Lower back
- Buttocks
- Thighs
Additional symptoms can include oily skin, acne, deep voice and irregular periods. It is caused by excess androgens, which is why these symptoms are similar to some of those found in PCOS. Effective treatment like Vaniqa (see below) can help combat symptoms, while tackling lifestyle factors like obesity can also help as obesity can be a factor in causing the condition. Excess hair growth is more common in women after the menopause.
HORMONE IMBALANCE FACIAL HAIR
Both of the above conditions involve excess levels of androgens, which are male hormones. This reflects the wider point that unwanted facial hair in women is usually a case of hormone imbalance. Testosterone is the most well-known androgen. In men, testosterone is involved in the production of sperm and the deepening of the voice.
All women produce some level of testosterone. However, producing excess levels of testosterone may produce effects like increased sex drive, menstrual cycle changes and excess facial and body hair.
This is partially why conditions like PCOS and hirsutism are more common in women who have experienced the menopause, as this change signals a dramatic shift in hormone balance.
HOW TO REMOVE FACIAL HAIR
Hormone imbalances in women can be difficult to treat. However, there are ways of treating the symptoms of these imbalances, such as unwanted facial hair. This can help women who are bothered by their excess facial hair feel more confident in their appearance, allowing you to enjoy your life without worry or self-consciousness.
FACIAL HAIR REMOVAL TREATMENT
Some women are happy to live with unwanted facial hair, but others wish to be rid of it. Effective hair removal medication does exist in the form of prescription creams. There are also other methods of removal which many people try, including bleaching, waxing, laser hair removal and electrolysis.
Not all of these methods are equal in terms of effectiveness and comfort, however. For example, both laser hair removal and electrolysis can be expensive and require multiple sessions. They can also be painful. We’ve outlined some of the most popular treatment methods below.
FACIAL HAIR REMOVAL CREAM
Facial hair removal cream is one of the most common treatment methods. Creams can cause the hair on the skin’s surface to dissolve, leaving the skin smooth. The effectiveness of this method is largely dependent on the brand chosen, as many products will not be as effective as they claim to be. Others however are proven in their effectiveness. To be safe, it is best to seek out a prescription medication like Vaniqa.
VANIQA
Vaniqa (eflornithine hydrochloride) is a prescription medication that was developed to reduce unwanted facial hair in women. Designed for application to the skin, it is advised that Vaniqa is only used on the face and adjacent areas under the chin of women affected by unwanted hair. It can take around 4-8 weeks for women to see the first signs that this medication is working – based on usage twice a day, at least 8 hours apart. It has been tested in women of multiple ethnicities, and has shown to be an effective treatment method.
Vaniqa works by slowing down the growth of facial hair by interfering with an enzyme in the follicle of the hair during the growth stage of the hair cycle. Without this enzyme the hair is unable to grow further.
FACIAL HAIR BLEACH
Some women may choose to bleach their facial hair rather than removing it. This can make the hair less noticeable by turning darker hairs a lighter shade. The pros of bleaching facial hair are that the process is fast, easy, affordable and can be done at home. However, it is not an effective choice for women seeking a smooth, hairless surface. It also isn’t a long-term solution, as you’ll see the return of the darker hair when it starts to grow. What’s more, it is only fully effective in disguising short, fine hairs.
WAXING FACIAL HAIR
Waxing is a longer-term solution than shaving or bleaching. Like bleaching, it can be done quickly and easily at home. It can also provide that smooth skin surface which many women look for. However, waxing can also be a painful process, and often leads to skin irritation. You’ll also have to regularly wax the skin in order to maintain the results, which can cause longer term irritation.
Sunburn is red, hot and sore skin caused by too much sun. It may flake and peel after a few days. You can treat it yourself. It usually gets better within 7 days.
How to ease sunburn yourself
Do
- get out of the sun as soon as possible
- cool your skin with a cool shower, bath or damp towel (take care not to let a baby or young child get too cold)
- apply aftersun cream or spray, like aloe vera
- drink plenty of water to cool down and prevent dehydration
- take painkillers, such as paracetamol or ibuprofen for any pain
- cover sunburnt skin from direct sunlight until skin has fully healed
Don't
- do not use petroleum jelly on sunburnt skin
- do not put ice or ice packs on sunburnt skin
- do not pop any blisters
- do not scratch or try to remove peeling skin
- do not wear tight-fitting clothes over sunburnt skin
You can ask a pharmacist:
- about the best sunburn treatments
- if you need to see a GP
Non-urgent advice:
See a GP urgently or call NHS 111 if:
- your skin is blistered or swollen
- your temperature is very high, or you feel hot and shivery
- you feel very tired, dizzy and sick
- you have a headache and muscle cramps
- your baby or young child has sunburn
Severe sunburn can lead to heat exhaustion and heat stroke, which can be very serious.
HOW DO YOU STOP SMOKING?
Recognising the dangers of smoking is the first step to quitting for good. There are several ways to go about kicking the habit, from behavioural therapy to nicotine replacement products. There is no single way for everyone to quit smoking. But it is important to note that, statistically, only between 4 and 7% of people who try to go cold turkey without help or support will succeed.
Medication such as Champix is a proven effective method for relieving cravings and symptoms of withdrawal by reducing your body’s reliance on nicotine. Champix is unique in that it uses the active ingredient varenicline, which bonds with nicotine receptors in the brain to reduce the sensations you experience when you smoke. Champix has been proven to help individuals stop smoking in just two weeks.
WHY IS IT SO DIFFICULT TO QUIT SMOKING?
Nicotine is the highly addictive drug contained within cigarettes. It affects many parts of your body, including your brain, and over time your body develops a tolerance to the substance which makes it difficult to abandon the habit completely. Evidence suggests that between 80 and 90% of people who smoke regularly live with a nicotine addiction.
Once ingested, nicotine reaches the brain within ten seconds and releases adrenaline, giving you a buzz of pleasant energy. Once a tolerance is developed, more and more nicotine is necessary to reach this buzz. As such, smokers become dependent on smoking and often turn to it when they are feeling sad, tired, irritable or stressed.
Over time, smoking becomes a physical habit which is hard to break, and individuals who have quit smoking often describe feeling restless and lacking in something to occupy their hands in the early stages of their giving up process.
WHAT DAMAGE DOES SMOKING CAUSE?
Smoking accounts for more than 80,000 deaths each year in England alone. This makes it the single biggest cause of preventable deaths. Half of all smokers will die from a smoking-related disease.
Smoking affects your circulation, as toxins from cigarettes enter your bloodstream. This then thickens the blood and increases your chances of clot formation, as well as increasing your blood pressure and heart rate. You will also experience a narrowing of the arteries, reducing the amount of oxygen-rich blood circulating to your organs. This combination of factors greatly increases your chances of developing heart disease or having a stroke.
Smoking has a negative impact on the health of your heart, stomach, skin, bones, brains and of course your lungs. As well as increasing your chances of coughs, colds and asthma, smoking also causes fatal conditions like pneumonia and lung cancer, as well as respiratory conditions like COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease).
In fact, smoking causes 84% of deaths from lung cancer and 83% of deaths from COPD.
WHY SHOULD YOU STOP SMOKING?
As soon as you stop smoking, you will begin to notice an improvement in your overall health and wellbeing. Stopping smoking:
- Helps you breathe more easily
- Gives you more energy
- Improves sexual performance (smoking increases the risk of erectile dysfunction in men between 30 and 50 years old by around 50%)
- Reduces feelings of stress
- Improves fertility (on average, women who smoke are only 72% as fertile as non-smokers)
- Slows facial ageing and decay
- Improves dental health
- Can add up to 10 years to your life (based on a man quitting at the age of 30).
You should also quit smoking for the benefit of those around you. Breathing in second hand smoke increases risks of lung cancer, heart disease and stroke, can be particularly damaging for any young children in your home.
If you have decided to quit smoking and looking for someone to help you on this journey then you have come to the right place. Research has shown that you are more likely to be successful at quitting smoking with counseling and Nicotine Replacement Therapies (NRTs) then try to quit without.
The benefits of quitting smoking are huge and it’s never too late to quit. It is a process which starts with you wanting to quit. There is a wide range of NRT products available to help you with quitting smoking. You can use a combination of products to help you overcome the nicotine cravings.
One of our team will help create a plan for you and have regular reviews with you to monitor your progress and to provide information and encouragement during this journey. We are passionate about helping our customers with quitting smoking as it has huge health benefits for the customer.
We stock some of the leading brands of NRT products such as Nicorette, Nicotinell, and Niquitin. The products are available in a range of different forms such as patches, chewing gum, lozenges, inhalators, nasal sprays, and microtabs. Come into our pharmacy or contact us for more details.
Sore throats are very common and usually nothing to worry about. They normally get better by themselves within a week.
How to treat a sore throat yourself
To help soothe a sore throat and shorten how long it lasts, you can:
- gargle with warm, salty water (children should not try this)
- drink plenty of water
- eat cool or soft foods
- avoid smoking or smoky places
- suck ice cubes, ice lollies or hard sweets – but do not give young children anything small and hard to suck because of the risk of choking
- rest
A pharmacist can help with sore throats
To help relieve the pain and discomfort of a sore throat, you can:
- use paracetamol or ibuprofen
- use medicated lozenges or anaesthetic sprays (although there's little proof they help)
You can buy them from a supermarket or from a pharmacist without a prescription.
See a GP if:
- your sore throat does not improve after a week
- you often get sore throats
- you're worried about your sore throat
- you have a sore throat and a very high temperature, or you feel hot and shivery
- you have a weakened immune system – for example, because of diabetes or chemotherapy
A severe or long-lasting sore throat could be something like strep throat (a bacterial throat infection).
Antibiotics
GPs do not normally prescribe antibiotics for sore throats because they will not usually relieve your symptoms or speed up your recovery.
They'll only be prescribed if your GP thinks you could have a bacterial infection.
Immediate action required:
Call 999 if:
- you have difficulty swallowing or breathing
- you're drooling
- you're making a high-pitched sound as you breathe (called stridor)
- your symptoms are severe and getting worse quickly
These symptoms can make breathing more difficult.
Causes and symptoms of sore throats
Sore throats are usually caused by viruses (like cold or flu) or from smoking. Very occasionally they can be caused by bacteria.
Symptoms include:
- a painful throat, especially when swallowing
- a dry, scratchy throat
- redness in the back of the mouth
- bad breath
- a mild cough
- swollen neck glands
The symptoms are similar for children, but children can also get a temperature and appear less active.
Conditions that can cause a sore throat
- laryngitis
- tonsillitis
- strep throat (a bacterial throat infection)
- glandular fever
We dispense private prescriptions from GMC registered doctors.
If you would like us to dispense your private prescription, please hand it in at the Pharmacy counter.
Private prescriptions are not subject to NHS charges, but you will have to pay for the medication itself. There are no exemptions for private prescriptions and all items will need to be paid for.
To get a price for your medication before you come to the Pharmacy, please call us on 020 7834 6050 or email us at info@geeschemist.net
WHAT IS PREMATURE EJACULATION?
Premature ejaculation is not an uncommon condition for men to experience at some point in their life. It refers to instances where a man comes to climax “too early some or most of the time” when they engage in sexual intercourse. However, the definition of what constitutes “too early” can change from individual to individual, though most professionals define premature ejaculation as when a man ejaculates after less than two minutes of being aroused.
Premature ejaculation can occur during all forms of sexual activity, including vaginal sex, anal sex, oral sex, masturbation and simple physical contact.
WHAT ARE THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PREMATURE EJACULATION AND ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION?
Erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation are often associated with one another, and can even be confused for each other, as they are both male sexual health conditions that relate to sexual activity and the male erection.
However, it is important to differentiate between the two conditions in order to select the most appropriate treatment. The main difference between the two conditions is that premature ejaculation is ejaculating too quickly, whilst erectile dysfunction (otherwise known as impotence) is an inability to achieve or maintain an erection.
If you still aren’t sure which condition you’re suffering from, speak to one of the Express Pharmacy team today using our discreet Live Chat service or by calling 0208 123 0703.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF PREMATURE EJACULATION?
It is currently difficult to gain a clear diagnosis of premature ejaculation, as the guidelines for what the specific symptoms of the condition are is often changing. This is largely due to the fact that all men have a different idea regarding how long sexual intercourse should last, so one man’s concerns may be non-existent in another man who ejaculates after the same period of time.
There has been no specific length established for how long sexual intercourse should last. However, studies into the conditions have set certain guidelines which allow us to establish two main symptoms of premature ejaculation. These include:
- Reaching the point of ejaculation within two minutes (120 seconds) or less of becoming aroused
- This problem occurring regularly. Most men will experience “one off” or intermittent instances of premature ejaculation at some point in their life.
The regular experience of reaching ejaculation within two minutes is the surest sign that you may potentially be suffering with premature ejaculation. However, it is still beneficial to discuss your symptoms with a medical professional in order to gain a clear diagnosis.
The embarrassment associated with premature ejaculation is common but often misplaced. Infrequent or intermittent premature ejaculation can be embarrassing and inconvenient, but it does not necessarily indicate a sexual dysfunction. Perhaps the surest sign of persistent premature ejaculation is where a man finds that the problem does not ease even when they have become comfortable with their sexual partner.
WHAT ARE THE CAUSES OF PREMATURE EJACULATION?
There are many factors which can be at the root of premature ejaculation, which is why so many men experience the condition. These causes can be both physical and psychological, or it can be brought on by lifestyle factors too.
Physical causes of premature ejaculation include:
- Spinal injuries
- Diabetes
- Vascular conditions
- Prostate disease
- High blood pressure
- Multiple sclerosis
- Neurological conditions
Psychological causes of premature ejaculation include:
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Guilt
- Nervousness
- A lack of confidence
- Unresolved emotional issues
- Sexual inexperience
Lifestyle factors which can contribute to premature ejaculation include:
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Drug use
- Nicotine
HOW TO TREAT PREMATURE EJACULATION
The first step to resolving your premature ejaculation is to understand what is causing the condition. This will give you a clue as to what method of treatment will benefit you. For example, if your premature ejaculation is simply due to nervousness, this will likely get better as you become more sexually confident.
Lifestyle changes can help reduce symptoms of premature ejaculation if the condition is indeed caused by lifestyle choices like drinking and drug use, whilst therapy or opening up to a partner can help alleviate premature ejaculation caused by psychological concerns. If the condition is caused by an underlying physical issue, treating this concern can help alleviate your premature ejaculation.
Prescription medication is an effective method of premature ejaculation relief, particularly SSRIs (Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors). Premature ejaculation medication such as Priligy uses the active ingredient Dapoxetine to encourage ejaculation delay during sexual intercourse.
A Guide to Pregnancy
During pregnancy it's completely normal to have many questions and concerns. Your local pharmacy is a great place to go for support during your pregnancy (and beyond), they'll help you you make the right choices when it comes to looking after your and your baby's health.
This is a very important stage on your life and it is normal to ask yourself a lot of questions and have many concerns. Do not worry, A pharmacist can support your way during pregnancy and beyond, making sure you make the right choices and helps you looking after your health and your baby.
Healthy eating
A healthy diet is a vital part of a healthy lifestyle at any time, but is especially important if you're pregnant or planning a pregnancy. Eating healthily during pregnancy will help your baby to develop and grow.
You don't need to go on a special diet, but it's important to eat a variety of different foods every day to get the right balance of nutrients that you and your baby need.
It's always best to get vitamins and minerals from the foods you eat, but when you're pregnant you need to take a folic acid supplement as well during the first few months, to make sure you get everything you and your baby may need.
There are also certain foods that should be avoided in pregnancy.
You will probably find that you are hungrier than usual, but you don't need to "eat for two" – even if you are expecting twins or triplets. This is one of the most common myths of pregnancy.
EXERCISE IN PREGNANCY
The more active and fit you are during pregnancy, the easier it will be for you to adapt to your changing shape and weight gain. It will also help you with labour and get back into shape after the birth of your baby.
Keep up your normal daily physical activity or exercise (sport, running, yoga, dancing, or even walking to the shops and back) for as long as you feel comfortable.
Exercise is not dangerous for your baby but there are certain exercises that should be avoided, so it is always worth to check with your Doctor or pharmacist.
Postnatal depression
Postnatal depression is a type of depression that many parents experience after having a baby. t's a common problem, affecting more than 1 in every 10 women within a year of giving birth. It can also affect fathers and partners, although this is less common.
It's important to seek help as soon as possible if you think you might be depressed, as your symptoms could last months or get worse and have a significant impact on you, your baby and your family.
It is difficult to understand if you are depressed as many women feel a bit down, tearful or anxious in the first week after giving birth. This is often called the "baby blues" and is so common that it’s considered normal as you need to adjust to your new situation and sometimes it can be challenging. The "baby blues" don’t last for more than two weeks after giving birth.
If your symptoms last longer or start later, you could have postnatal depression. Postnatal depression can start any time in the first year after giving birth.
How can we help you?
Request a one to one consultation with one of our pharmacist who can answer your questions and give you advice about.
- Healthy eating in pregnancy
- Exercise in pregnancy
- Medicines in pregnancy. What can you take to ease your symptoms and which medicines you need to avoid.
- Post-natal depression
Piles (haemorrhoids) are lumps inside and around your bottom (anus). They often get better on their own after a few days. There are things you can do to treat and prevent piles.
Check if it's piles
Symptoms of piles include:
- bright red blood after you poo
- an itchy anus
- feeling like you still need to poo after going to the toilet
- slimy mucus in your underwear or on toilet paper after wiping your bottom
- lumps around your anus
- pain around your anus
How you can treat or prevent piles
Do
- drink lots of fluid and eat plenty of fibre to keep your poo soft
- wipe your bottom with damp toilet paper
- take paracetamol if piles hurt
- take a warm bath to ease itching and pain
- use an ice pack wrapped in a towel to ease discomfort
- gently push a pile back inside
- keep your bottom clean and dry
- exercise regularly
- cut down on alcohol and caffeine (like tea, coffee and cola) to avoid constipation
Don't
- do not wipe your bottom too hard after you poo
- do not ignore the urge to poo
- do not push too hard when pooing
- do not take painkillers that contain codeine, as they cause constipation
- do not take ibuprofen if your piles are bleeding
- do not spend more time than you need to on the toilet
Ask a pharmacist about treatment for piles
A pharmacist can suggest:
- creams to ease the pain, itching and swelling
- treatment to help constipation and soften poo
- cold packs to ease discomfort
Many pharmacies have private areas if you do not want to be overheard.
See a GP if:
- there's no improvement after 7 days of treatment at home
- you keep getting piles
Your GP may prescribe stronger medicines for haemorrhoids or constipation.
Ask for an urgent GP appointment or call 111 if:
- you have piles and your temperature is very high or you feel hot and shivery and generally unwell
- you have pus leaking from your piles
Hospital treatment for piles
If there's no improvement to your piles after home treatments, you may need hospital treatment.
Talk to your doctor about the best treatment for you. Treatment does not always prevent piles coming back.
Treatment without surgery
Common hospital treatments include:
- rubber band ligation: a band is placed around your piles to make them drop off
- sclerotherapy: a liquid is injected into your piles to make them shrink
- electrotherapy: a gentle electric current is applied to your piles to make them shrink
- infrared coagulation: an infrared light is used to cut the blood supply to your piles to make them shrink
You'll be awake for this type of treatment, but the area will be numbed.
You should be able to go home on the same day.
If these treatments do not work, you may need surgery to remove your piles.
Surgery
Surgical treatments include:
- haemorrhoidectomy: your piles are cut out
- stapled haemorrhoidopexy: your piles are stapled back inside your anus
- haemorrhoidal artery ligation: stitches are used to cut the blood supply to your piles to make them shrink
You'll usually need to be asleep for this type of treatment and may need to stay in hospital for more than 1 day.
If Immediate action required, go to A&E or call 999 if you have piles and:
- you're bleeding non-stop
- there's a lot of blood – for example, the toilet water turns red or you see large blood clots
- you're in severe pain
What causes piles?
Piles are swollen blood vessels. It's not clear what causes them.
Things that make piles more likely:
- constipation
- pushing too hard when pooping
- pregnancy
- heavy lifting